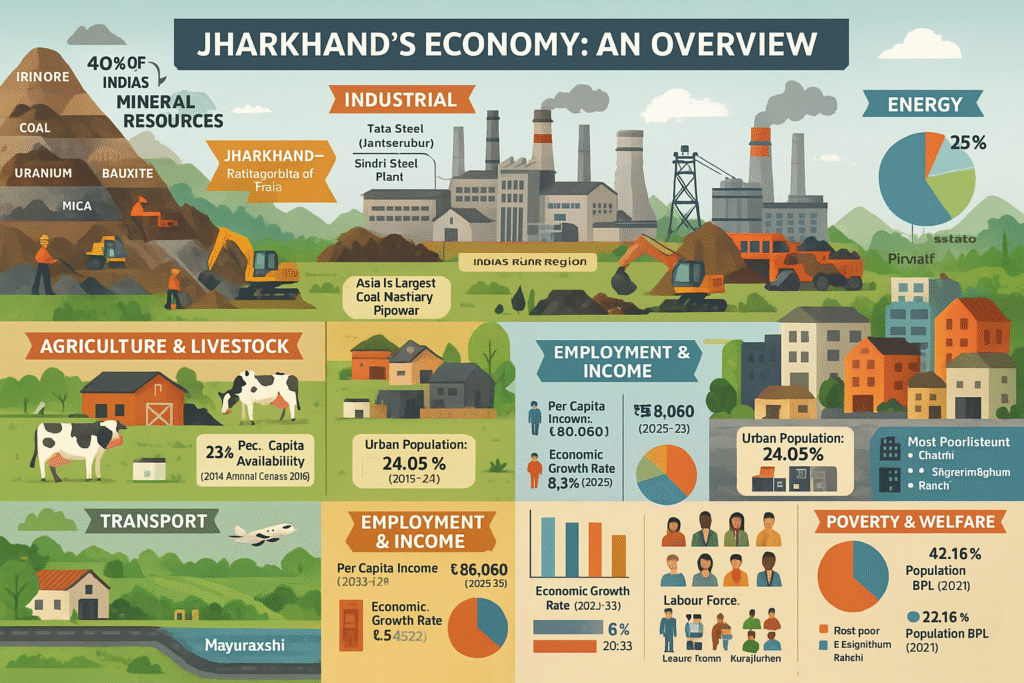
Jharkhand, established in 2000, is rich in natural resources and has vast potential for industrial growth. Recognizing this, the state has launched three key industrial policies—in 2001, 2012, and 2016—each building upon the last to transform Jharkhand into an attractive destination for investors and entrepreneurs.
Jharkhand Industrial Policy, 2001
Notified: 1 March 2001
Significance: First industrial policy after state formation
Main Objectives:
- Rapid development of basic infrastructure
- Reduction in unemployment
- Promotion of domestic and foreign investment
- Balanced regional development
- Encouragement of private sector participation
- Boost to small and cottage industries
- Promotion of research & development for productivity
Key Achievements:
- Establishment of mega, large, medium, and small industries
- Increase in industrial output, state revenue, and GSDP
- Creation of industrial employment opportunities
Institutions Behind Implementation:
- Ranchi Industrial Area Development Authority (RIADA)
- Adityapur Industrial Area Development Authority (AIADA)
- Bokaro Industrial Area Development Authority
- Infrastructure Development Corporation
- State Khadi Board
- Jharcraft
Due to the policy’s success, a new policy was introduced in 2012 to address evolving challenges and opportunities.
Jharkhand Industrial Policy, 2012
Scope: Five-year implementation
Total Objectives Identified: 16
Major Objectives:
- Encourage investment and continuous industrial development
- Support manufacturing & processing industries
- Promote sericulture, handloom, khadi, and village industries
- Conserve and support rural handicrafts
- Establish coordination between large, small, and micro industries
- Rational use of mineral and natural resources
- Promote horticulture and food processing
- Encourage eco-friendly technology and skills
- Ensure inclusive industrial participation (SC/ST/Backward Classes)*
- Foster modernization and technological upgrades
- Bridge regional disparities within the state
- Establish PPP-based industrial parks
- Promote private education investment (technical, medical, management)
- Boost human resource and skill development
- Create a fear-free, investor-friendly environment
- Promote transparent law & governance systems
Implementation Strategy:
- Special incentives for private industries, clusters & parks
- Single Window Clearance System for speedy approvals
- Focus on infrastructure development
- Promotion of Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs)
- Market support for small-scale & handicraft products
- Special Economic Zones (SEZs) for steel, ICT, automobiles, processing
- Identification & revival of sick industries
- Update to the 2008 Rehabilitation & Resettlement Policy
- Special incentives for SC/ST/Women/Persons with Disabilities
- Development of district-level land banks
- Creation of industrial corridors with integrated infrastructure
- Parks for textile, IT, herbs, food, pharma via PPP
- SEZ for automobile industry in Adityapur
- Establishment of Industrial Area Development Authorities
- Expansion of technical institutions (25% seat reservation for state residents)
- Setup of Mini Tool Rooms in Ranchi & Dumka
- Proposal for NRI Cells in Ranchi and Delhi*
- Proposal for Investor Meets (e.g., Momentum Jharkhand)
Jharkhand Industrial & Investment Promotion Policy, 2016
Duration: Five years
Focus: Infrastructure, Innovation, Inclusion, Employment & Transparency
Primary Goals:
- Position Jharkhand as a trusted investment destination
- Promote sustainable industrial growth
- Develop web-based transparent project approvals
Execution Strategy:
- Encourage innovation and connect regional value chains
- Promote private & PPP investment in infrastructure (roads, energy, parks)
- Train rural women SHGs in sericulture, handicraft, handloom
- Provide timely credit to MSMEs
- Develop international trade facilitators
- Strengthen Single Window System for export industries
- Ensure land availability & management for investors
- Special support to Women, SC, and ST entrepreneurs
- Build robust monitoring, evaluation & grievance systems
- Launch skill development programs across the state
- Accelerate infrastructure development
- Promote labour-intensive industries
- Focus on industrially backward districts
- Enhance area-specific vocational training
- Encourage universities for Start-ups & Innovation
- Support tech upgrades & R&D
- Promote e-Governance & ease of doing business
- Reform labour laws with a focus on women
- Adopt a focused approach for “Make in India”
Policy Duration & Applicability
- Effective from April 1, 2021
- Valid for five years
Vision & Core Objectives
The policy envisions building a conducive and modern industrial climate to:
- Attract investments through proactive and transparent governance
- Promote innovation and boost global competitiveness
- Facilitate adoption of Industry 4.0 and emerging technologies
- Enable grassroot capacity building for sustainable industrial growth
- Ensure rapid and sustained growth in the industrial sector to increase its share in the Gross State Domestic Product (GSDP)
Key Measures to Achieve These Goals:
- Establish an effective and supportive institutional framework
- Build and implement robust promotion strategies
- Develop warehouses, common facilities, and logistics hubs
- Strengthen marketing support, R&D, and quality testing labs
Major Policy Highlights
High Priority Sectors Identified:
- Textile & Apparel
- Automobile & Auto Components
- Food & Meat Processing
- Pharmaceuticals
- Electronic System Design & Manufacturing (ESDM)
Capital Investment Incentives:
- Capital investment incentives up to 25% or a maximum of ₹6.25 crore
- For Micro Industries: Incentive on investment up to ₹1 crore
- For Small Industries: Incentive on investment up to ₹10 crore
- For Large Industries: Incentive on investment up to ₹25 crore
- All women entrepreneurs receive an additional 5% incentive
Strategic Vision & Goals
- Create an enabling ecosystem with strong infrastructure to attract investors
- Promote innovation and global competitiveness
- Equip industries for adoption of new-generation technologies
- Strengthen grassroots capacity to ensure sustainable development
- Achieve fast-paced and sustainable industrial growth over the next decade
Key Policy Objectives
- Attract ₹1 lakh crore in investments
- Generate 5 lakh employment opportunities
- Make Jharkhand a preferred investment destination
- Promote sustainable industrial development
Support System Development:
- Web-based time-bound transparent approval system for:
- Project approvals
- Production declarations
- Financial and non-financial assistance
- Strengthening core infrastructure, including:
- Warehouses
- Inland Container Depots (ICDs)
- Cold Storages
- Road-Rail connectivity for industrial clusters
- Tool Rooms and Testing Labs
Focus on Export & MSME Integration
- Emphasis on export-oriented industries
- Special focus on 100% indigenously manufactured export goods in the MSME sector
- Develop linkages between OEMs and MSME/ancillary units
Implementation & Development Strategy
Infrastructure Development:
- Promote private investment and PPP models for infrastructure:
- Roads
- Electricity
- Telecommunications
- Industrial estates, clusters, and parks
- Support rural industrialization through:
- Sericulture
- Khadi & Handicrafts
- Food Processing
- Handloom
- Bamboo, Leather, and Lac-based industries
Credit & Financial Support:
- Ensure timely and adequate credit availability for industries, especially MSMEs
Institutional & Governance Reforms
- Establish strong networks with Export Promotion Councils, ITPO, regional & MSME associations
- Develop International Trade Service Providers to enhance global business
- Strengthen Single Window Clearance System to assist export-oriented industries
- Improve land management systems to ensure availability of plots/land for new investors
Inclusive Industrial Development
- Provide special incentives for:
- Women entrepreneurs
- Scheduled Castes (SC)
- Scheduled Tribes (ST)
- Institutionalize grievance redressal, monitoring, and evaluation systems
- Create consultative mechanisms with stakeholders and industrial associations
Entrepreneurship & Skill Development
- Emphasize entrepreneurship training and skill enhancement
- Strengthen vocational and technical training in industrial backward areas
- Promote labour-intensive industries to generate employment
Technology, Innovation & R&D
- Encourage startups, innovation hubs, and technology transfer
- Incentivize universities for R&D, product development, and tech upgrades
- Provide support for traditional sectors like:
- Mineral-based products
- Handicrafts
- Handloom
- Agro-based and processed food products
Agro & Food Processing Development
- Enhance processing levels to reduce wastage and promote value addition
- Improve income of farmers and boost exports in the sector
Digital Governance & Ease of Doing Business
- Promote business facilitation, e-governance, and digitized services
- Introduce labour reforms to support business-friendly laws and women participation
- Adopt a focused “Make in India” approach