Explore the comprehensive infrastructure development of Jharkhand, including major airports, expressways, industrial corridors, Bharatmala projects, and Gati Shakti terminals—crucial facts for competitive exams and regional planning insights.
Key Facts and Introduction
- As per the Jharkhand Economic Survey 2022–23, the road density in the state stands at 168.7 km per 1000 sq. km.
- In 2021, the density was 162.27 km, showing an increase of 6.43 km per 1000 sq. km.
- The target is to increase this to 250 km per 1000 sq. km by 2025.
- The State Highways Authority of Jharkhand (SHAJ) was established in 2015 for the development and strengthening of state roads and highways.
Modes of Transport in Jharkhand
1. Road Transport
(a) National Highways (NH)
- Definition: National highways are major roads connecting multiple states or crucial locations within a state.
- Responsibility:
- Selected by: State Government.
- Declared by: Central Government.
- Maintenance: Fully funded by the Central Government.
- Total Length (as of August 2022): 3,340 km (as per Economic Survey 2022–23).
- Longest National Highway in Jharkhand:
- NH-20 (new designation) with a length of 391.6 km, passing through 6 districts: Koderma, Hazaribagh, Ramgarh, Ranchi, Khunti, and West Singhbhum.
- Replaces NH-33 (old designation), which was earlier the longest with 333 km, also covering 6 districts.
- Exam Fact: NH-20 passes through the maximum number of districts in Jharkhand.
Major National Highways after Renumbering
| S.No. | New NH | Old NH | Route (Key Places) | Length (in km) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 114A | 32, 33, 6, 5 | Sarath, Madhupur, Giridih, Dumri | 298.0 |
| 2 | 118 | 32 | Chandil, Ghatshila | 215.5 |
| 3 | 19 | 63 | Jamshedpur | 17.0 |
| 4 | 419 | 5 | Marhi, Bagodar, Govindpur | 199.82 |
| 5 | 20 | 23, 31, 33, 75 | Koderma, Barhi, Hazaribagh, Ranchi, Khunti, Chakradharpur | 391.6 |
| 6 | 220 | 23 | Chaibasa, Govindpur | 54.0 |
| 7 | 320 | 23 | Ramgarh, Gola, Chas | 80.30 |
| 8 | 22 | 19, 30, 99 | Hunterganj, Chatra, Chandwa | 106.0 |
| 9 | 522 | 100 | Chatra, Hazaribagh, Bagodar | 120.0 |
| 10 | 133 | 31, 80, 110 | Sahibganj, Rajmahal, Barharwa | 92.9 |
| 11 | 133A | – | Godda, Chopa | 123.0 |
| 12 | 133B | – | Barharwa, Pakur | 11.0 |
| 13 | 333 | – | Sahibganj | 20.0 |
| 14 | 333A | – | Deoghar | 97.5 |
| 15 | 39 | 75, 76 | Godda, Sundarpahari, Littipara, Pakur | 261.0 |
| 16 | 139 | 86, 98 | Rajhara, Chhatarpur, Hariharganj | 55.4 |
| 17 | 43 | – | Gumla, Ranchi, Mandar, Manikui, Satyasheelachaya | 274.0 |
| 18 | 143 | 23 | Palkot, Kolebira, Betnagar | 122.0 |
| 19 | 143A | – | Gumla, Ghaghra, Lohardaga | 71.0 |
| 20 | 343 | – | Garhwa | 48.5 |
| 21 | 49 | 6, 23, 200 | Baharagora | 23.6 |
| 22 | 143H | – | Salangabahal, Bihabandh, Litebeda | 6.50 |
| 23 | 143D | – | Jamatoli, Basia, Kamdara, Torpa, Khunti | 81.70 |
| 24 | 320G | – | Hatgamharia, Jagannathpur, Barai, Manoharpur, Anandpur | 226.0 |
| 25 | 143AG | – | Kolebira | 180.0 |
| 26 | 320D | – | Chakradharpur, Sonua, Goelkera, Manoharpur, Saraikela | 134.5 |
| 27 | 218 | – | Chandanikiyari, Jharia, Dhanbad | 99.7 |
| 28 | 143B | – | Govindpur, Dumri, Mahuadand | 44.4 |
- Important Exam Fact: NH-19 is part of India’s Golden Quadrilateral Project.
Other Modes of Transport in Jharkhand
2. Rail Transport
(Details not provided in the original section but significant in state logistics.)
3. Air Transport
(Only mentioned but not elaborated upon in the text.)
4. State and International Highways
- State Highways: Managed by SHAJ since 2015.
- International Roads: The mention of Asian Highway (AH2100) indicates international connectivity, especially with South-East Asia via border routes.
Highlights for Exams
- SHAJ was formed in 2015 to oversee road development.
- NH-20 is currently the longest National Highway in the state.
- Road density increased by 6.43 km/1000 sq. km. between 2021 and 2022.
- Target road density for 2025: 250 km/1000 sq. km.
- NH-19 is part of the Golden Quadrilateral – a national highway development milestone.
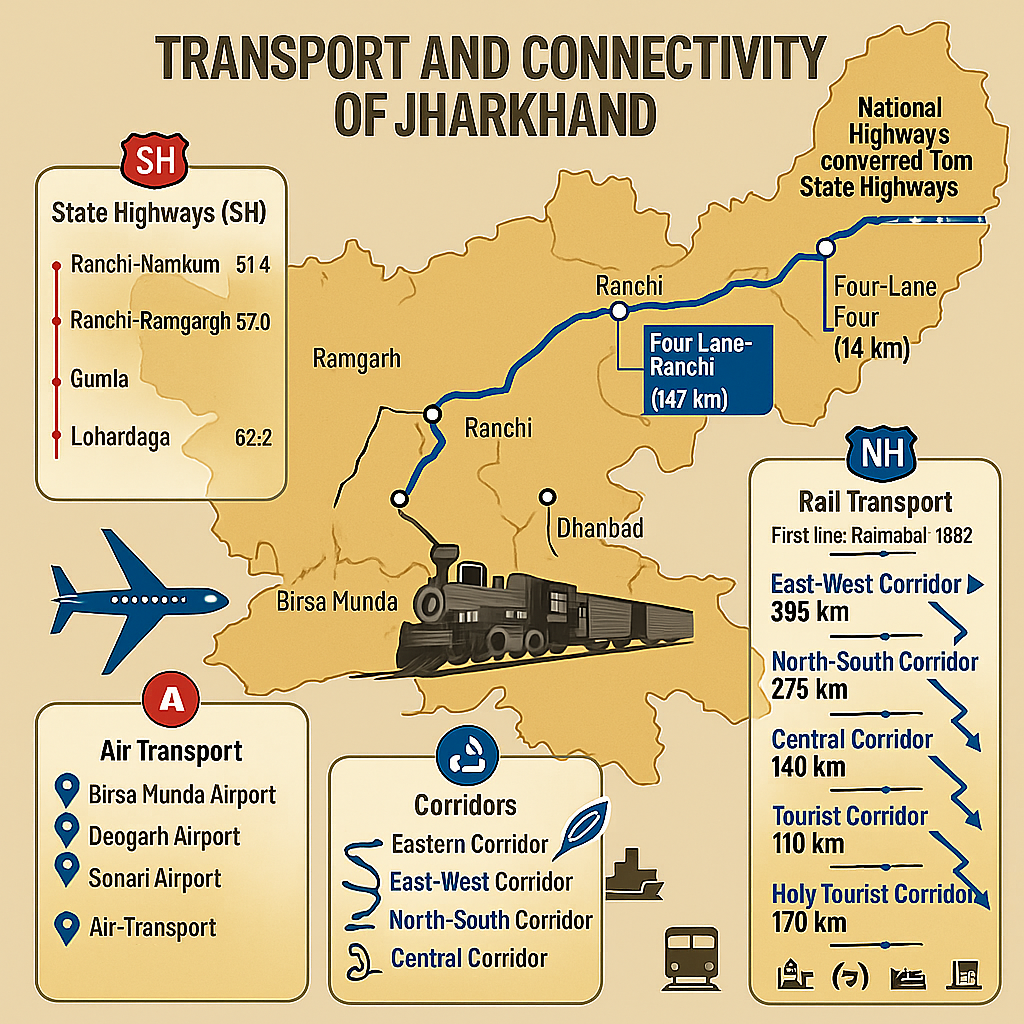
Transport Infrastructure in Jharkhand (State Highways, Railways, Air Transport)
State Highways in Jharkhand
- Definition: Roads connecting the state capital to district headquarters are known as State Highways.
- Maintained by: State Government of Jharkhand.
- Total length of State Highways: 1,231.9 km
(Source: Jharkhand Economic Survey 2022–23)
Key State Highways and Their Lengths (in km):
- Ranchi – Namkum – Tatisilwe – Angara – Silli – Muri: 61.4 km
- Ranchi – Kanke – Patratu – Bhurkunda – Ramgarh: 57.0 km
- Tamar – Arki – Khunti – Basia – Kolebira: 125.0 km
- Kolebira – Bano – Gua – Jamda – Noamundi – Gamharia: 83.0 km
- Adityapur – Kandra – Seraikela – Chaibasa: 67.0 km
- Jamshedpur – Hata – Chaibasa: 62.2 km
- Hazaribagh – Barkagaon – Tandwa – Rakhelgadi – Tangar Mod: 75.0 km
- Kudu – Lohardaga – Ghaghra – Gumla: 71.0 km
- Bhusar – Mahuadanr – Netarhat – Bishunpur – Ghaghra: 182.0 km
- Medininagar – Lesliganj – Panki – Hariharganj – Balumath: 93.0 km
- Garhwa – Ranka – Godarmana – Ramanujganj: 61.6 km
- Dhanbad – Patardih – Chandan Kiyari – Chas: 60.0 km
- Koderma – Jamua – Tundi – Govindpur: 156.0 km
- Dumri – Giridih – Bengabad – Madhupur – Deoghar: 153.0 km
- Deoghar – Saraiyabad – Godda – Pathargama – Mahagama – Pirpainti: 155.0 km
- Deoghar – Chaupa – Jama – Amatara – Rupnarayanpur: 139.0 km
- Bhagalpur – Hansdiha – Lakdapahari – Dumka – Rampurhat: 102.0 km
- Dumka – Kathikund – Gopikandar – Amrapara – Barhait – Sahibganj: 183.0 km
- Total Length of all major State Highways: 1,886.4 km
- Converted into National Highways: 654.5 km
- Remaining State Highways: 1,231.9 km
Important:
State Highways 5, 8, 11, 14, 15, 16, and 17 have been converted into National Highways.
International Highway
- Proposed by ECAFE (Economic Commission for Asia and the Far East): Total 63,500 km length.
- Will pass through Barhi (Jharkhand).
- Total Indian stretch: 2,680 km.
- Connects:
- Amritsar → Delhi → Agra → Kanpur → Kolkata → Dhaka
- Agra → Gwalior → Hyderabad → Bangalore → Dhanushkodi
- Barhi → Kathmandu
- Countries Covered: Singapore, Thailand, Myanmar, Bangladesh, India, Pakistan, Turkey.
- This road will link the Asian Highway to the European International Highway.
Rail Transport in Jharkhand
- Total railway length in Jharkhand: 2,394.46 km
(Source: indianrailways.gov.in)
Historical Highlights:
- 1862: First railway line from Kolkata to Rajmahal.
- 1907: Purulia–Ranchi railway line initiated.
- 1911: Ranchi–Lohardaga rail line constructed.
Railway Zones:
- East Central Railway (ECR) – HQ: Hajipur
- South Eastern Railway (SER) – HQ: Kolkata
(Formerly Bengal–Nagpur Railway)
Railway Divisions:
- Dhanbad Division (formed: 5 Nov 1951) – under ECR
- Ranchi Division (formed: 1 Apr 2003) – under SER
- Chakradharpur Division (formed: 14 Apr 1952) – under SER
- Dhanbad is the highest revenue-generating station in the state.
- High-density rail coverage in Damodar Valley and Subarnarekha Valley.
- Rail-deficient regions: Palamu plateau, Upper Damodar valley, Hazaribagh plateau, Rajmahal hills.
Key Projects:
- Koderma–Giridih: 111 km
- Koderma–Hazaribagh–Ranchi: 203 km
- Lohardaga–Ranchi (via Tori): 113 km
- Koderma–Tilaiya: 14 km
- Deoghar–Dumka–Rampurhat: 124 km
Institutional Support:
- Formation of Jharkhand Central Railway Limited (JCRL) to speed up projects.
- Land acquisition underway for Shivpur–Kathautia railway project.
- Formation of Jharkhand Rail Infrastructure Development Corporation Limited (JRIDCL) – a 51:49 Joint Venture between State Govt. and Rail Ministry.
Projects under JRIDCL:
- Namkum – Kandra
- Giridih – Parasnath – Madhuban
- Tori – Chatra
- Chatra – Basukinath
- Godda – Pakur
Eastern Dedicated Freight Corridor (EDFC):
- Total Length: 1,856 km
- 196 km of the corridor passes through Jharkhand
Air Transport in Jharkhand
- First airport established in Ranchi (1941)
- Birsa Munda Airport, Ranchi: Only International Airport in Jharkhand
- Other Airports:
- Jamshedpur – Sonari Airport
- Dhanbad, Bokaro
- Dumka – Sidho-Kanho Airport
- Maithon Airport
- Deoghar Airport – Fully operational
- Foundation laid: 25 May 2018 by PM Narendra Modi
- Inaugurated: 12 July 2022 by PM Modi
- Tripartite agreement among GoJ, AAI, DRDO
Aviation Training & Development:
- Gliding centers operational at Ranchi and Jamshedpur
- New gliding centers at Dumka and Dhanbad
- Planned aviation academies in Giridih and Bokaro
- Commercial Pilot License Academy to be set up at Dumka in PPP mode with Aryan Aviation Pvt. Ltd.
Note: All facts marked with an asterisk () have been previously asked in various Jharkhand competitive exams.*
Air Transport in Jharkhand
- Under the Regional Connectivity Scheme (UDAN), Dumka and Bokaro have been selected for development.
- For the first time, a flight landed at Sonari Airport, Jamshedpur.
- During World War II, the British company constructed an airstrip in Chakulia (East Singhbhum) to counter Japanese forces.
- In 1944–45, the British government built airstrips at Nawadih for the Burma campaign.
List of Airports in Jharkhand
| S.No | Airport Name | Location |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Birsa Munda Airport | Ranchi |
| 2 | Deoghar Airport | Deoghar |
| 3 | Sonari Airport | Jamshedpur |
| 4 | Dhalbhumgarh Airport | Jamshedpur |
| 5 | Bokaro Airport | Bokaro |
| 6 | Dhanbad Airport | Dhanbad |
| 7 | Maithon Airport | Dhanbad |
| 8 | Sidho-Kanhu Airport | Dumka |
Major Highway and Infrastructure Projects
- Ranchi–Bokaro Expressway project to begin under PPP mode in the upcoming fiscal year.
- The state government proposes a Golden Triangle with a 6-lane expressway linking Jamshedpur, Dhanbad, and Ranchi.
- Under the Bharatmala Project, NH-75 (now NH-31) is included:
- Construction of a 203 km four-lane road from Kudu to Daltonganj (Medininagar) via Uttar Pradesh.
- A 147 km road between Sambalpur and Ranchi has also been approved.
Gati Shakti & Railway Developments
- India’s first PM Gati Shakti Cargo Terminal has been launched at Thapar Nagar Station, Dhanbad (Asansol Division).
- Chakradharpur Railway Station is named after Raja Chakradhari Singhdev of Porahat.
- Adityapur Railway Station is named after Raja Aditya Pratap Singhdev of Saraikela.
Jharkhand Corridor Projects
- Total sanctioned corridor length: 1,367 km of four-lane roads.
- A total of 6 high-speed international-level corridors are to be constructed.
Details of the Proposed 6 Corridors
| Corridor Name | Length (km) | Route Details |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Eastern Corridor | 121 | Sahibganj → Nirsa → Sindri → Chandanakiyari → Chandil |
| 2. East-West Corridor | 393 | Mudisemar (Garhwa) → Chatra → Bengabad → Madhupur → Sarath → Palojori → Dumka |
| 3. North-South Corridor | 275 | Barlanga → Silli → Ranchi |
| 4. Central Corridor | 140 | Budhmu → Tandwa → Chatra → Hunterganj → Dobhi (Bihar Border) |
| 5. Tourist Corridor | 270 | Milanchowk (Silli-Rangamati Rd) → Saraikela → Tamad → Khunti → Govindpur → Sisai |
| 6. Holy Tourist Corridor | 170 | Jhumritilaiya → Vishnugarh → Petarwar → Kasmar → Gola → Dumri → Rajrappa → Deoghar → Giridih |
Important Exam-Oriented Highlights
- Birsa Munda Airport, Ranchi is Jharkhand’s only international airport.
- Deoghar Airport became operational and was inaugurated by PM Modi on July 12, 2022.
- Jharkhand Central Railway Limited (JCRL) formed for accelerating rail projects like Shivpur–Kathotia.
- Joint venture company formed with 51:49 stake between State and Ministry of Railways: Jharkhand Rail Infrastructure Development Corporation Limited.
- Jamshedpur, Dhanbad, and Ranchi to be developed as an Industrial Corridor.
- NH-75 (now NH-31) and Sambalpur–Ranchi road included in Bharatmala Pariyojna.
