Discover the comprehensive overview of Jharkhand’s Power and Energy Infrastructure, including major hydroelectric projects, thermal power plants, renewable energy potential, and state-led energy initiatives, crucial for competitive exams and policy insights.
Installed Power Capacity of Jharkhand
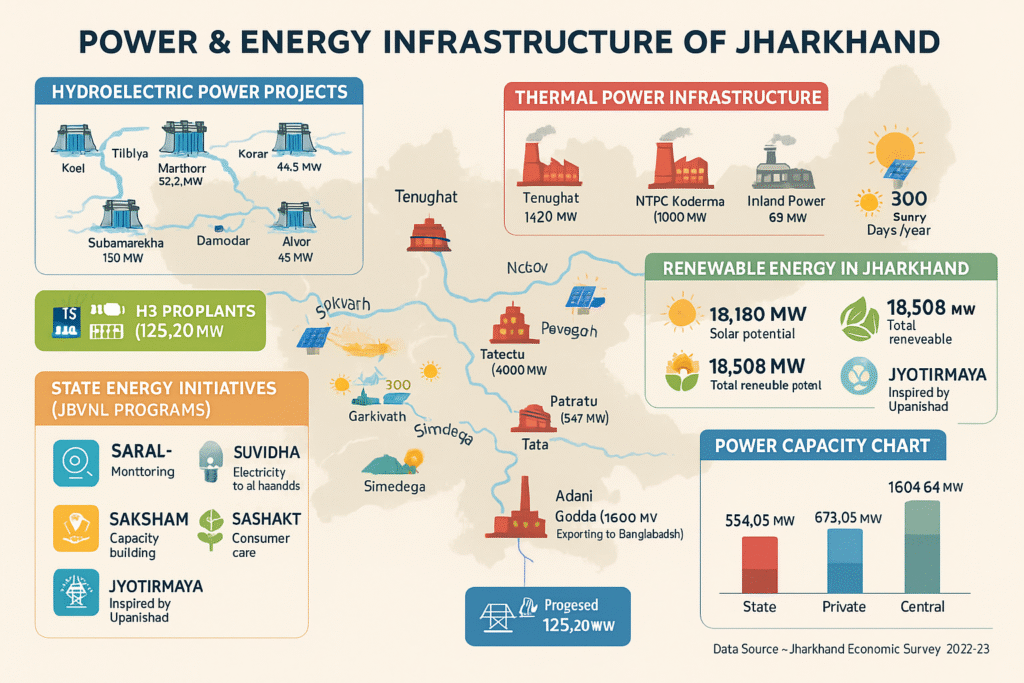
According to the Jharkhand Economic Survey 2022–23, the total installed power generation capacity of the state is 2735 MW, categorized as follows:
- Central Government: 55.13%
- Private Sector: 24.61%
- State Government: 20.26%
Energy Type Classification:
- Coal-based (Thermal): 89%
- Hydro-based: 7%
- Renewable Energy: 4%
Types of Power Projects in Jharkhand
- Thermal Power Projects (TPPs)
- Hydro Power Projects (HPPs)
Thermal Power Projects in Jharkhand
1. Bokaro Thermal Power Station
- First coal-based thermal power station under Damodar Valley Corporation (DVC).
- Located on Bokaro River, a tributary of Damodar.
- Production started in 1953.
- Installed capacity: 500 MW.
- Supplies power to the National Grid.
2. Chandrapura Thermal Power Station
- Established in Bokaro by DVC in 1965.
- Total capacity: 500 MW (2 units of 250 MW each).
3. Koderma Thermal Power Station
- Located at Banjeridih, Jayanagar Block, Koderma.
- Operated by DVC.
- Capacity: 1000 MW (2 units of 500 MW).
- Uses bituminous coal for power generation.
4. Patratu Vidyut Utpadan Nigam Ltd. (PVUNL)
- Located in Patratu, Ramgarh district.
- Established on 15 October 2015.
- Joint venture between NTPC (74%) and JBVNL (26%).
- Built along the Nalkari River.
Key Highlights:
- Planned total capacity: 4000 MW.
- Phase 1: 3 units of 800 MW.
- Phase 2: 2 units of 1800 MW.
- Electricity distribution: Jharkhand (85%), Bihar (688 MW), Odisha (396 MW), West Bengal (99 MW).
- Coal supplied from Banharadih coal block.
- Water sourced from Patratu Dam (27 cusecs).
- Funding: 75% loan to NTPC and 25% to JBVNL via Rural Electrification Corporation.
- Earlier plant (1973) supported by Russia under 4th Five-Year Plan.
- Old plant (840 MW) supplied power to HEC, Hatia, Ranchi.
5. Tenughat Thermal Power Station
- Near Tenughat Dam, Bokaro district.
- Installed capacity: 420 MW.
- Operated by Tenughat Vidyut Nigam Ltd. (TVNL), incorporated under Companies Act, 1956.
- HQ located in Hinoo, Ranchi.
6. North Karanpura Thermal Power Station
- Located in Tandwa, Chatra.
- Being developed by NTPC.
- Total proposed capacity: 1980 MW (3 units of 660 MW).
7. Adani Power Ltd.
- Located in Godda district on 425 acres.
- Part of Special Economic Zone (SEZ).
- Approved investment: ₹14,000 crore.
- Capacity: 1600 MW.
- Exports 1496 MW power to Bangladesh Power Board.
8. Tata Power Ltd.
- Located in Jojobera (Jamshedpur).
- Acquired a 67.5 MW unit from Tata Steel.
9. Inland Power Ltd.
- Located in Gola, Ramgarh.
- Production capacity: 63 MW.
- Power supplied to Jharkhand Bijli Vitran Nigam Ltd. (JBVNL).
10. Modern Power Ltd.
- Located in Palampur and Shrirampur villages of Seraikela-Kharsawan.
- Production capacity: 270 MW.
Hydro Power Projects in Jharkhand
1. Tilaiya Hydel Power Station
- Located on Barakar River, Koderma.
- Established in 1953 by DVC.
- Capacity: 4 MW (2 x 2 MW).
2. Maithon Hydel Power Station
- Located on Barakar River, Dhanbad.
- Established in 1957 by DVC.
- Only gas-turbine based plant in Jharkhand.
- First of its kind in Southeast Asia.
- Total capacity: 63.2 MW (2 units of 20 MW, 1 unit of 23.2 MW).
3. Swarnarekha Hydel Project
- Located on Swarnarekha River, Ranchi district.
- Established in 1989 with World Bank assistance.
- Joint project of Jharkhand, West Bengal, and Odisha.
- Power supplied to Ranchi industries via Hatia Grid.
4. Konar Hydel Power Station
- Located on Konar River, Bokaro.
- Capacity: 40 MW.
- Has underground generation facilities.
5. Aiyar Hydel Project
- Located on Damodar River.
- Installed capacity: 45 MW.
6. Panchet Hydel Project
- On Damodar River, near Dhanbad–Purulia border.
- Capacity: 80 MW (2 x 40 MW units).
7. Bal Pahari Hydel Project
- Located on Barakar River, Giridih district.
- Capacity: 20 MW.
Proposed Hydro Power Plants in Jharkhand
A total of 13 new hydroelectric power plants are proposed with an investment of ₹1052 crore. Details are as follows:
| Project Area | River | Capacity (MW) | Cost (₹ Crore) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Torpa | Karo | 13 | 128.5 |
| Kurdega | |||
| Dasham Falls | Kanchi | 6 | 53.64 |
| Manoharpur | Koel-Karo | 8 | 89.79 |
| Basin | Koel | 9 | 106.17 |
| Jonha Falls | Swarnarekha | 1 | 7.98 |
| Sita Falls | Swarnarekha | 0.7 | 6.35 |
| Adki D Falls | Tajna | 1.5 | 11.94 |
| Swarnarekha | 11 | 37.91 | |
| Shankh/Brahmani | 19 | 166.08 |
Key Takeaways for Competitive Exams
- Patratu, Maithon, Chandrapura, Tenughat, and Bokaro are crucial thermal power stations.
- Maithon Gas Turbine Station is unique in Southeast Asia.
- Swarnarekha Project is a tri-state collaboration with World Bank support.
- Adani Power (Godda) supplies power to Bangladesh.
- Proposed hydro projects cover all major rivers including Koel, Karo, Swarnarekha, and Shankh.
- Renewable energy still constitutes a small share (4%) of the energy mix.
Hydroelectric Power Projects in Jharkhand (Proposed & Existing)
- Sugabandh-1 & Sugabandh-2 (Budha/Northern Koel River)
- Capacity: 4.5 MW each
- Annual Generation: 36 MUs and 39.49 MUs respectively
- Itangar Project (Shankh/Brahmani River)
- Capacity: 24 MW
- Annual Generation: 196.85 MUs
- Another project on Shankh/Brahmani
- Capacity: 23 MW
- Annual Generation: 171.97 MUs
- Total 13 hydroelectric power plants proposed with combined capacity of 125.20 MW
- Estimated cost: ₹1052.67 crore
- To be installed on various rivers of Jharkhand
- Hydroelectric power cost is less than ₹1 per unit
Koel-Karo Hydropower Project (Proposed)
- Will be developed by National Hydroelectric Power Corporation (NHPC)
- Located on Koel and Karo rivers
- Districts involved: Ranchi, Gumla, West Singhbhum
- Total capacity: 732 MW
- Phase I: 710 MW
- Phase II: 22 MW
- (Frequently asked in competitive exams)
Major Hydroelectric Projects in Jharkhand
| Project Name | Capacity | District | River |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tilaiya Hydel Plant | 4 MW | Koderma | Barakar |
| Maithon Hydel Plant | 63.2 MW | Dhanbad | Barakar |
| Subarnarekha Hydel Project | 130 MW | Ranchi | Subarnarekha |
| Konar Hydel Plant | 40 MW | Bokaro | Konar |
| Panchet Hydel Plant | 40 MW | Dhanbad | Damodar |
| Bal Pahadi Hydel Plant | 20 MW | Giridih | Barakar |
| Aiyar Hydel Plant | 45 MW | — | Damodar |
Installed Power Capacity in Jharkhand (in MW)
| Ownership/Source | Thermal | Hydro | Renewable | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| State | 420.00 | 130.00 | 40.05 | 554.05 |
| Private | 580.00 | 0.00 | 93.09 | 673.09 |
| Central | 1446.50 | 61.00 | 97.14 | 1604.64 |
| Total | 2446.50 | 191.00 | — | 2734.64 |
(Source: Jharkhand Economic Survey 2022–23)
Facts asked in exams are marked with an asterisk.
New Initiatives by Jharkhand Bijli Vitran Nigam Ltd. (JBVNL)
- SARAL–SAMIKSHA:
- An online project monitoring tool for real-time tracking of running projects and transformer repair.
- SUVIDHA:
- Implemented under Saubhagya Scheme to provide universal household electrification by 2018
- SAKSHAM:
- Aims to enhance the skill and productivity of employees in the power department.
- SASHAKT:
- Ensures high-quality consumer services and provides a tech-enabled complaint platform.
- JYOTIRMAYA:
- Inspired by Bṛhadāraṇyaka Upanishad’s Shanti Mantra; defines roles of energy corporations in sectors:
- Jharkhand Urja Vikas Nigam Ltd. – Holding
- Jharkhand Urja Utpadan Nigam Ltd. – Generation
- Jharkhand Urja Sanchar Nigam Ltd. – Transmission
- Jharkhand Urja Vitran Nigam Ltd. – Distribution
- Inspired by Bṛhadāraṇyaka Upanishad’s Shanti Mantra; defines roles of energy corporations in sectors:
Major Power Generation Units in Jharkhand
| Company | Mode | Supply Capacity | Areas Covered |
|---|---|---|---|
| Damodar Valley Corporation (DVC) | Coal | 1050 MW | Bokaro, Chandrapura |
| Tata Power Co. | Thermal | 547 MW (Jojobera) | — |
| Hydro | 80 MW (Panchet) | — | |
| Hydro | 104 MW (Tilaiya) | — | |
| Thermal | 120 MW | — | |
| Tenughat Vidyut Nigam | Coal | 420 MW | — |
| NTPC (Koderma) | Coal | 1000 MW | — |
| Inland Power Ltd. | Coal | 63 MW | — |
| Patratu Vidyut Nigam | Coal | 4000 MW (planned) | — |
Facts frequently asked in state-level exams
Other Notable Power Sector Facts
- Coal India Ltd. has 3 major subsidiaries operational in Jharkhand:
- CCL, BCCL, and ECL
(Unique to Jharkhand)
- CCL, BCCL, and ECL
- Adani Group’s 1600 MW power plant being developed in Godda, will export electricity to Bangladesh
- Ultra Mega Power Projects (UMPPs):
- 17 UMPPs identified in Jharkhand
- 9 granted approvals
- Tilaiya UMPP – first of Jharkhand
- Hussainabad (Deoghar) – location of second UMPP
Renewable Energy in Jharkhand
- Excellent solar radiation:
- Over 300 sunny days/year, average 4–5 hours/day of sunlight
- Estimated solar power potential:
- 18,180 MW
- Total renewable energy potential (including biomass, mini-hydro, waste-to-energy):
- 18,508 MW
- DVC’s Solar Installations:
- Koderma: 1.162 MW
- Maithon (Dhanbad): 0.102 MW
Solar Park Scheme in Jharkhand
- Launched: 12 December 2014
- Target Capacity (Initially): 20,000 MW
- Revised (2017): 40,000 MW
- By 2021–22: 50 solar parks were planned nationwide
Approved Solar Parks in Jharkhand (As of Dec 31, 2021)
| S. No. | Solar Park Name | Capacity (MW) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Floating Solar Park | 100 |
| 2 | Devgarh Solar Park | 20 |
| 3 | Palamu Solar Park | 20 |
| 4 | Garhwa Solar Park | 20 |
| 5 | Simdega Solar Park | 20 |
Star-marked points indicate those frequently asked in exams.
