Discover a comprehensive overview of Jharkhand’s economy, welfare schemes, agriculture, food security, urban development, and industrial growth (2025) — essential for students, exam aspirants, and policy enthusiasts seeking accurate, updated insights into the state’s socio-economic progress.
1. Macro-Economic Overview Gross Value Added (GVA) Growth by Sector (Constant Prices) Sector/Sub-sector 2019–20 2020–21 2021–22 Agriculture, Forestry & Fishing 6.8% 14.0% Mining and Quarrying -18.2% -0.6% Primary Sector (1+2) -3.8% 8.8% Manufacturing 0.3% 5.2% Electricity, Gas, Water Supply, etc. -6.4% 12.2% Construction -8.0% 10.9% Secondary Sector (3+4+5) -2.3% 7.0% Trade, Repair, Hotels & Restaurants -19.7% 12.3% Transport, Storage, Communication -17.3% 4.6% Financial Services 5.5% 6.0% Real Estate, Dwelling Ownership, Prof. Svcs. -3.1% 6.8% Public Administration 1.9% 3.4% Other Services 8.6% 0.1% Tertiary Sector (6 to 11) 7.6% -5.6%
2. GSVA, GSDP, and Per Capita Income (₹ in Crores) At Constant and Current Prices Year GSVA (Const.) GSVA (Current) GSDP (Const.) GSDP (Current) PCI (Const.) PCI (Current) 2011–12 139130 139130 150918 150918 ₹41,254 ₹41,254 2018–19 206619 278824 229274 305695 ₹56,133 ₹75,421 2019–20 205900 283196 231755 310305 ₹55,658 ₹75,016 2020–21 (P) 197297 275019 218962 300716 ₹51,365 ₹71,071 2021–22 (Pr) 212308 315164 236816 343178 ₹55,126 ₹78,660 2022–23 (Pr) 230391 349932 255372 381125 ₹58,819 ₹86,060
Growth Analysis
CAGR (2011–12 to 2018–19):
GSVA: 6.2% ,
GSDP: 6.2% ,
PCI: 7.9%
Growth from 2020–21 to 2021–22:
GSDP at constant prices: 8.2%
GSVA at constant prices: 7.6%
Estimated GSDP for 2023–24 (Constant Prices): ₹2,74,154 crore
Estimated GSDP Growth (2023–24): 1.4%
3. Sectoral Contributions to GSVA (2021–22) Sector Growth (2020–21) Growth (2021–22) Share in GSVA Agriculture & Allied 6.8% 14.0% 14.7% Mining & Quarrying -18.2% -0.6% 7.2% Primary Sector -3.8% 8.8% 21.8% Secondary Sector -2.3% 7.0% 33.6% Tertiary Sector -8.7% 7.5% 44.6%
Highest growth sector : Agriculture, Forestry & Fishing (14% )Negative growth : Mining and Quarrying (-0.6% )
4. Jharkhand vs. India – Economic Comparison Year India Growth Rate Jharkhand Growth Rate 2011–12 to 2014–15 6.4% 7.3% 2015–16 to 2018–19 7.2% 9.4% 2019–20 3.7% 1.1% 2020–21 -6.6% -5.5%
Jharkhand’s share in national GDP has been 1.6% since 2017–18.
5. Per Capita Income (PCI)
2000–01 : ₹9,980 (Rank 25 out of 28)2011–12 : ₹41,254 (Rank 24 out of 29)2020–21 : ₹51,365 (constant), ₹71,071 (current)2022–23 : ₹58,819 (constant), ₹86,060 (current)Rank : 26th among 28 states in PCIOnly Uttar Pradesh and Bihar have lower PCI.
Goa has the highest PCI: ₹2,98,527 (Goa’s PCI is 481.2% higher than Jharkhand).
6. Inflation in Jharkhand Year Jharkhand Inflation India Inflation 2016–17 5.3% 4.5% 2017–18 3.9% 3.6% 2018–19 3.9% 3.5%
Post-October 2019, inflation rose above 6% RBI limit .
In 2022 , inflation was above 6% for most months (except July, Nov, Dec).
7. Multidimensional Poverty in Jharkhand
Source : NITI Aayog’s MPI Baseline Report (2019–21)Poverty dropped from 42.16% (2015–16) to 36.6% (2019–21)
Indicator 2015–16 2019–21 MPI 0.246 0.183 Rural MPI 0.202 0.160 Urban MPI 0.067 0.046 Poverty Headcount Ratio (%) 50.93% 43.8% Poverty Intensity (%) 44.24% 41.5%
8. Fiscal Health & Budget Trends
Budget grew 13 times between 2001–02 (₹6,000 Cr) and 2021–22 (₹78,000 Cr)
Average Annual Growth : 13.6%14th Finance Commission (2015–16 to 2019–20): 6.8% budget growthRevenue Surplus : Recorded between 2015–22, except 2020–21 (Covid lockdown year)Fiscal Deficit :
2015–16: 5.58% (due to UDAY scheme loan of ₹5,553 Cr)
2020–21: 4.96%
2021–22: 0.76%
2022–23 (Est.): 2.96%
Per Capita Debt (2019–20) : ₹25,000
9. Institutional Finance in Jharkhand
Total Bank Branches (2022) : 3,210
Scheduled Commercial Banks: 2,535 (79%)
Regional Rural Banks: 443 (14%)
Cooperative Banks: 117 (3.5%)
Small Finance Banks: 115 (3.5%)
Branch Growth (2021–22) :
Commercial banks: -0.7%
Small finance banks: +27.8%
District with Most Branches : Ranchi (14% of total)ATM Growth (2014–15 to 2021–22) :
Jharkhand: 3.87% CAGR
India: 2.87% CAGR
10. PM-KISAN Scheme in Jharkhand
As of 4 Nov 2022 , 31.01 lakh farmers benefitted under the PM-KISAN scheme.
Key Takeaways for Exam Aspirants
PCI of Jharkhand ranks 26th among 28 states.
Primary sector contributed 21.8% , tertiary 44.6% , secondary 33.6% to GSVA.Highest growth in agriculture (14%) and trade/services (12.3%) .
Multidimensional poverty declined from 42.16% to 36.6% .Banking growth and financial penetration have improved, esp. SFBs .
Veer Shaheed Poto Ho Khel Vikas Yojana
A scheme under MGNREGA to develop sports infrastructure across the state.
Target: Develop ~5,000 sports grounds across Jharkhand.
Status:
4,398 locations identified.
Work initiated at 3,791 locations.
1,279 grounds completed.
Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana (PMGSY)
33,053 km of rural roads approved in Jharkhand.
Completed: 27,663 km of rural roads.
Best performing districts: Gumla, Giridih .
Worst performing: Dhanbad, Koderma .
Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana – Gramin
Objective: Provide pucca houses with toilets, electricity, and clean water by 2022.
Cost-sharing: 60:40 between Centre and State.
Target: 16,03,268 houses.
Completed: 14,00,304 houses (87%).
Social Assistance Programs
National Social Assistance Schemes
Scheme Beneficiaries Benefit Indira Gandhi National Old Age Pension BPL aged 60–79: ₹200/month, 80+ years: ₹500/month Widow Pension Scheme BPL widows aged 40–59: ₹200/month Disability Pension Scheme Disabled persons aged 18–59: ₹200/month National Family Benefit Scheme On death of BPL breadwinner (18–64 years): ₹10,000 (one-time) Annapurna Scheme BPL senior citizens not covered under pensions: 10 kg food grains/month
Total beneficiaries under these schemes: 33.47 lakh .
Female beneficiaries: 58.31% .
Aadhaar verification completed for 94% of beneficiaries.
Jharkhand-Specific Social Pension Schemes
Scheme Beneficiaries Monthly Pension Vivekananda Nishakt Swavalamban Yojana Disabled: ₹1,000 Rajya Samajik Suraksha Vridhavastha Pension Senior citizens (rural <₹10,500; urban <₹12,500 income): ₹600 Aadim Janjati Pension Particularly vulnerable tribal groups (PVTGs): ₹600 Widow Respect Pension Scheme Widows: ₹600 AIDS/HIV Pension ₹600
Jharkhand Integrated Adarsh Gram Yojana (JIGAY)
Integrated initiative combining:
MP Adarsh Gram
PM Adarsh Gram
CM Smart Panchayat
MLA Adarsh Gram Yojana
Jharkhand State Livelihood Promotion Society (JSLPS)
Focus: Poverty alleviation, women empowerment, equity.
Introduced Bank Sakhi Model for SHG involvement in banking.
Example: Soni Kumari from Jokho village (Keredari block) appointed as Bank Correspondent Sakhi.
Goat-Based Livelihood Program
“Livestock Sakhi” trained to support SHGs in goat, poultry, and duck rearing.
2022–23: 1,610 families linked to animal-based livelihoods.
Mahila Kisan Sashaktikaran Yojana
Objective: Empower women through sustainable agriculture investments.
Focus areas:
Non-Agricultural Activities by JSLPS
Startup Village Entrepreneurship Program (SVEP) Palash Brand : State-supported brand for SHG products promotion & marketing.
Skill Development and Placement (JSLPS)
DDU-GKY (Deendayal Upadhyaya Grameen Kaushal Yojana):
Targets rural youth (15–35), STs, transgenders, trafficking victims.
Age limit extendable to 45 years.
RSETI : Rural Self Employment Training Institutes provide vocational skills.
JHIMDI Project (Horticulture via Micro Drip Irrigation)
Funded by Japan, aimed at sustainable agriculture via drip irrigation.
Coverage: 9 districts, 30 blocks.
Support for SHG members and leased landholders.
JOHAR Project (World Bank Assisted)
Jharkhand’s Opportunities for Harnessing Rural Growth Targets:
2 lakh rural households
3,500 producer groups
20 producer companies
Operating in 17 districts, 68 blocks.
Goal: Double rural income via:
Collective production & marketing
Value addition & financial access
Market linkage
Entrepreneurship
Panchayati Raj and Governance Reforms
Structure
24 Zila Parishads, 264 Panchayat Samitis, 4,345 Gram Panchayats.
Urban: 9 Corporations, 20 Municipalities, 20 Nagar Panchayats.
50% of elected representatives in panchayats are women.
Infrastructure:
396 Panchayat Libraries
1214 Computers
Internet in 1326 panchayats
CSCs in 1155 panchayats
Central Finance Commission Grants
15th Finance Commission recommends:
75% of grants to rural local bodies (FY 2021–22 & 2022–23).
Chapter 7 of its report titled “Empowering Local Governments” .
PESA Implementation
131 blocks in 16 districts under PESA.
13 districts fully covered; 3 partially (Palamu, Garhwa, Godda).
National Gram Swaraj Abhiyan
Timeframe: 1 April 2018 – 31 March 2022.
Focus: Strengthening PRIs in 117 aspirational districts to meet SDGs.
Panchayat Awards 2022
Award Winner Panchayat Deendayal Panchayat Empowerment Award Murhu, Dumaria, Bangarkala Nanaji Deshmukh National Gaurav Gram Sabha Award Bangarkala (Giridih) Gram Panchayat Development Plan Award Kapilo (Birni block, Giridih) Bal Mitra Gram Panchayat Award Bundu (Petarwar block, Bokaro)
Panchayat Citizen Charter
Motto: “Meri Panchayat Mera Adhikar – Jan Seva Hamare Dwaar”
99.86% panchayats drafted charters.
99.38% charters approved.
SWAMITVA Scheme (Drone-based Land Survey)
Launched: 24 April 2021.
Objectives:
Ownership record (Record of Rights)
Easier bank loans
Reduced land disputes
Implementation:
Out of 32,712 villages, 757 notified.
Drone survey completed in 240 villages.
Urban Development Highlights
Urban Population Share in Jharkhand : 24.05% vs. national average 31.1%.Most Urbanized Districts :
Dhanbad (58.1%)
East Singhbhum (55.6%)
Bokaro (47.7%)
Least Urbanized : Godda (4.9%).Slum Population : 3.73 lakh.
72.4% in Class-I cities.
Highest concentration: Ranchi (19.9%) .
Socio-Economic Profile of Jharkhand (2021–2022)
Economic Indicators (as per 2020–2021 data)
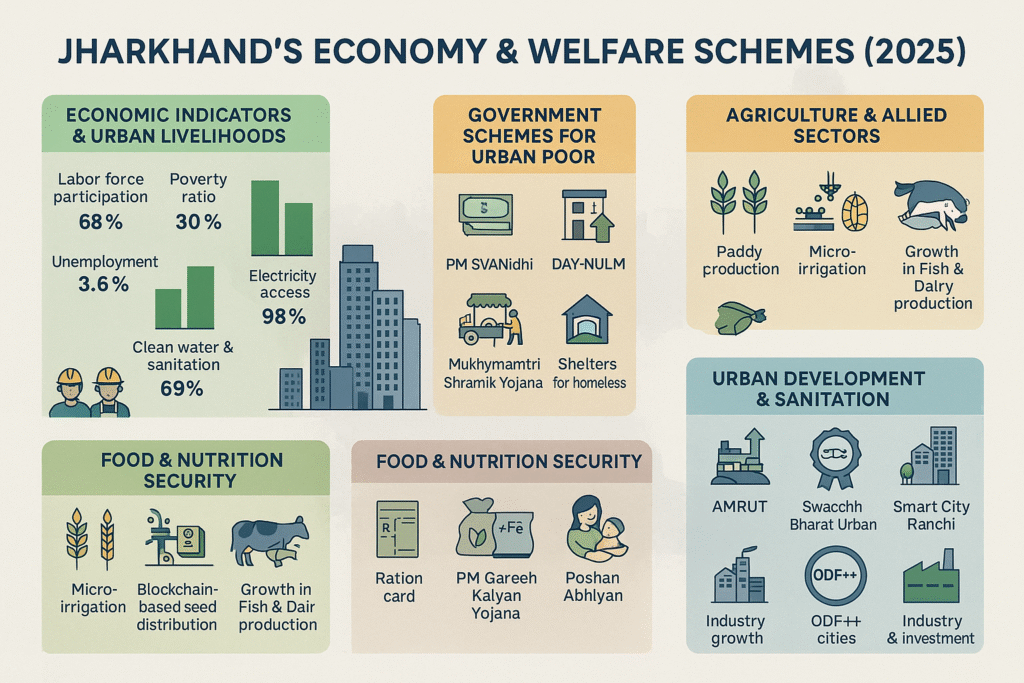
Labour Force Participation Rate :
Overall: 41.9%
Urban: 59.6%
Unemployment Rate (2019–20) :
Overall: 9.3%
Urban: 3.1%
Poverty Headcount Ratio (2011–12) :
Multidimensional Poverty Index (2019–21) :
Overall: 36.6%
Urban: 11.1%
Social Indicators
Female Literacy (2019–21) :
Rural: 61.7% , Urban: 80.1%
Male Literacy (2019–21) :
Rural: 81.3% , Urban: 92.0%
Neonatal Mortality Rate : 22.2% Infant Mortality Rate : 37.9% Under-5 Mortality Rate : 45.4% Children under 5 who are underweight : 39.4%
Housing Indicators
Electricity Access :
Urban: 99.0% , Overall: 94.3%
Access to Safe Drinking Water :
Urban: 86.6% , Overall: 75.9%
Sanitation Facility Access :
Urban: 75.9% , Overall: 56.7%
Use of Clean Fuel :
Urban: 71.0% , Overall: 31.9%
Urban Livelihood & Infrastructure
National Urban Livelihood Mission (DAY–NULM)
Started in 2013 , replacing the SJSRY.
Focuses on skill development and self-employment of the urban poor .
Major Components:
Social Mobilization & Institution Development
Skill Training & Placement
Self-Employment Program
Street Vendor Support
Shelters for Urban Homeless
Mukhyamantri Shramik Yojana
Launched in August 2020 by Jharkhand Govt.
Focused on returning migrant workers post COVID-19.
Offers 100 days of unskilled wage employment annually.
PM SVANidhi Yojana
Full Form: Pradhan Mantri Street Vendors AtmaNirbhar Nidhi
Launched: June 1, 2020
Offers:
₹10,000 collateral-free loan for street vendors (1 year term)
7% interest subsidy on timely repaymentAccess to future loans of ₹20,000 and ₹50,000
Integrated with 8 central welfare schemes under “SVANidhi se Samriddhi”
Drinking Water and Sanitation
Urban Water Access
Only 21.2% of urban families have tap water connections at home (as of August 2022).
91% have toilet access in urban areas.
Swachh Bharat Mission – Urban
Phase 1 : 2 Oct 2014 – 30 Sep 2021
Goal: 100% Open Defecation Free (ODF) urban areas
Phase 2 (SBM-Urban 2.0) : Launched Oct 1, 2021
Goal: 100% waste-free cities
Swachh Survekshan 2022 – Achievements:
Jharkhand ranked 2nd nationally
Chaibasa (pop: 50k–1 lakh): Best Citizen Feedback AwardBundu (pop: 15k–25k): Best Citizen Feedback AwardJamshedpur : Declared cleanest city with 3-star rating 15 ULBs declared ODF , 23 as ODF+ , and 3 (Jamshedpur, Medininagar, Sahebganj) as ODF++
AMRUT Mission (Atal Mission for Rejuvenation and Urban Transformation)
Launched in 2015 to improve urban infrastructure and services
7 Jharkhand cities covered :AMRUT 2.0 launched in Oct 2021 to focus on:
Urban water supply
Water body rejuvenation
Green space development
Namami Gange Project
Launched: June 2014 , with ₹20,000 crore allocation
Objectives:
Pollution abatement , Ganga river rejuvenation Includes: STPs, solid waste mgmt., riverfronts, e-flow, afforestation
Jharkhand received ₹250 crore by Oct 2022
Saturday – No Car Initiative
Started in Ranchi, March 2021
Citizens encouraged to use bicycles instead of motor vehicles
Public Bike Sharing (PBS) launched in 2019 with 600 cycles at 60 stations
Urban Health Initiatives
Schemes:
Ayushman Bharat National Urban Health Mission Atal Clinics (Goal: 100 clinics; 99 functional by Sep 2022 )
Districts with most clinics:
East Singhbhum (17), Dhanbad (12), Ranchi (12)
Urban Beautification & Environment
35 Parks developed under AMRUT across 7 ULBs (5 per ULB)
13 water bodies rejuvenated :
Hazaribag (9), Basukinath (3), Dhanbad (1 – Rajendra Sarovar)
Ranchi Smart City Project
Selected on May 25, 2016
Greenfield project at HEC area (656.3 acres)Ranchi received Smart Cities Leadership Award along with Ahmedabad & Varanasi
Agriculture & Allied Activities
Key Programs
Seed Distribution (using Blockchain ) – first in India
Jharkhand Farm Loan Waiver Scheme
Krishi Samriddhi Yojana, Birsa Pathshala, Agri Clinics, Farmers’ Helpline
Land Use & Ownership
Net sown area : 17% (13.28 lakh ha)Forest area : 28%Fallow land :
Current: 17%,
Other fallow: 13%
Landholding Patterns
Type of Landholding % of Total Holdings Marginal (<1 ha) 70% Small + Marginal (<2 ha) 85% Semi-medium (2–4 ha) 10% Medium (4–10 ha) 5% Large (>10 ha) 1%
Crop Production & Productivity (2021–22)
Kharif Crops
Rice: 5,365.17 thousand tonnes | Productivity: 3042 kg/ha
Maize: 606.43 thousand tonnes | Productivity: 2225 kg/ha
Rabi Crops
Wheat: 519.36 thousand tonnes | 2282 kg/ha
Pulses: 449.70 thousand tonnes | 3853 kg/ha
Oilseeds: 364.86 thousand tonnes | 2271 kg/ha
Cropping Intensity reduced from 140.8 (2017–18) to 135.8 (2021–22)
Irrigation
Focus on micro-irrigation : Drip (59%), Sprinkler (41%)
Micro-irrigation covers 43,399 ha
Irrigation sources :
Wells: 37%
Ponds: 30%
Other: 31%
Canals: 2%
Agriculture Finance
Credit flow growth: 9.91% (2021–22 to 2022–23)
All KCC accounts upgraded to Smart KCC with ATM access
Horticulture: Vegetables & Fruits
Vegetable production :
2017–18: 34.75 lakh tonnes → 2021–22: 38.18 lakh tonnes
Top: Potato (6.99L t) , Peas (4.29L t) , Cabbage (3.20L t)
Fruit production :
2017–18: 10.81 lakh tonnes → 2021–22: 13.12 lakh tonnes
Top: Mango , Jackfruit
Dairy Development in Jharkhand
In 2001–02 , daily milk production in Jharkhand was 25.75 lakh liters , which increased to 59.80 lakh liters in 2019–20 .
Per capita milk availability rose from 96 grams/day (2001–02) to 182 grams/day (2019–20), marking a 90% growth .Total milk production was 23.21 lakh metric tonnes in 2019–20 , with a target of 33.67 lakh metric tonnes by 2023–24 .
Fisheries Production
Fish production grew from 1.9 lakh tonnes (2017–18) to 2.5 lakh tonnes (2021–22) .
Major Agricultural Schemes and Initiatives
Seed Distribution and Exchange Program :
Jharkhand became India’s first state to use blockchain technology (via SettleMint) for seed distribution.
Jharkhand Agriculture Loan Waiver Scheme :
Launched in 2020–21 with ₹2,000 crore budget.
Up to ₹50,000 of crop loan waived per standard account .
1.34 lakh beneficiaries in 2021–22 and 3.94 lakh in 2022–23 .
e-NAM (National Agriculture Market) :
19 wholesale markets in Jharkhand registered under e-NAM.Hazaribagh market is the most active , with ₹7.65 crore in trade.
Birsa Crop Expansion Scheme :
Provides subsidized seeds to farmers.
₹20 crore allocated.
Integrated Birsa Village cum Farmer School :
Launched on 15 August 2021 to train farmers in agriculture, fisheries, piggery.
₹90 crore allocated.
Jharkhand State Crop Relief Scheme :
Replaces PMFBY from 2020–21 .
Provides compensation for crop loss due to natural disasters.
Initial fund: ₹2,100 crore .
Food and Nutritional Security
NFSA State Ranking Index 2022 :
Jharkhand ranked 10th out of 20 states/UTs .
Best performer in NFSA Coverage .
Ranks: Delivery (14), Nutrition Initiative (5).
Storage & PDS Infrastructure
Highest rice stock : East SinghbhumWheat : DumkaSalt : LateharSugar : Dhanbad25,094 PDS dealers , out of which 23,761 are online-enabled .Districts with most PDS dealers:
Ranchi (2,134) , Giridih (2,133) , Dhanbad (1,627) Least: Lohardaga (398)
89% of ration shops are privately operated , 11% by SHGs .
Ration Card Types
Pink – PHHYellow – AAYGreen – Neither PHH nor AAYWhite – For households with annual income above ₹1 lakh
Distribution of Commodities through PDS (Jan–Dec 2022)
Grains (Rice + Wheat) : 2,448.5 thousand tonnes
Top districts: Giridih, Ranchi, Dhanbad
Salt : Ranchi, Palamu, HazaribaghSugar : Giridih, Sahibganj, PalamuKerosene : Ranchi, Giridih, Deoghar
Key Food Security & Nutrition Initiatives
CM Petrol Subsidy Scheme (2022) :
₹250/month for two-wheeler fuel to eligible NFSA beneficiaries.
Pulse Distribution Scheme :
PMGKAY (till Dec 2022) :
5 kg extra food grain/month free to NFSA beneficiaries.
Jharkhand State Food Security Scheme :
For non-NFSA individuals.
5 kg grains/month at ₹1/kg.
Cap increased from 15 lakh to 20 lakh beneficiaries in 2022–23.
Dakeya Yojana (2017) :
35 kg grains/month free to 73,891 PVTG families.
Rice Fortification Scheme :
Implemented in 22 districts .
Highest coverage: Hazaribagh, Dhanbad, Ranchi
Annapurna Scheme :
10 kg rice/month free for elderly not covered under IGNOAPS .
AAY Sugar Distribution Scheme :
Sugar at subsidized rate; subsidy: ₹18.50/kg by GoI
Salt Distribution :
Free refined iodized salt to PHH & AAY families.
Kerosene Distribution Scheme :
Kerosene at subsidized price; direct benefit transfer (DBT) used.
CM Daal-Bhaat Scheme
₹5 per meal for the poor.
377 centers and 11 night meal centers operational.Pilot CM Canteens operational in Ranchi & Jamshedpur.
Jharkhand State Contingency Food Fund
Established in 2018–19 .
Provides 10 kg free/discounted rice during emergencies.
Sona Sobran Dhoti-Sari Distribution Scheme
Annual distribution (twice a year) of subsidized clothes (dhoti, sari, lungi) to NFSA beneficiary households.
Nutrition Security
POSHAN Abhiyan (launched 8 March 2018):
For children, pregnant women, and lactating mothers .
Implemented in all 24 districts .
SAAMAR (launched March 2021):
Targets malnutrition & anemia.
SAAMAR App used by teams to track beneficiaries.Targets:
Children (0–9 yrs) Adolescent girls (10–19 yrs) Women (20–24 yrs) Pregnant & lactating women
Thematic Events under POSHAN:
Gender-sensitive water management
Women’s health
Traditional nutrition education
Nutrition & education integration (e.g., Poshan bhi, Padhai bhi )
Best-performing districts: Gumla, Deoghar, Dumka
PM POSHAN (formerly Mid-day Meal Scheme)
Covers classes 1 to 8 in all government and aided schools.
Mortality Rate (NFHS-5, 2019–21)
Indicator Jharkhand (Total) India (Total) Under-5 Mortality Rate 45.4 41.9 Neonatal Mortality 28.2 24.9 Infant Mortality Rate 37.9 35.2 Maternal Mortality Rate (SRS 2018–20) 56 per lakh 97 per lakh
Industry and Manufacturing in Jharkhand
The state government has framed multiple policies to boost industrial and manufacturing growth .
Industries contribute significantly to GSDP and employment generation.Industrial units grew by 0.6% between 2018–19 and 2019–20.In 2021–22 , ₹48 crore (US $6 million) of FDI was received.
From Oct 2019 to June 2022 , the state received ₹19,290 crore (US $2.656 billion) in FDI.
Read more about :- Jharkhand Economic Survey 2022–23: A Detailed Analysis

One thought on “Jharkhand Economic Survey 2022–23: A Detailed Analysis”