Discover a complete guide to Local Governance and Constitutional Provisions in Jharkhand , covering Panchayati Raj, Urban Administration, Scheduled Areas, and key constitutional articles—essential for UPSC, JPSC, and state exam preparation.
Introduction to Local Governance in Jharkhand
Local governance in Jharkhand is divided into:
Rural Administration (Panchayati Raj) Urban Administration (Municipal Governance)
Key structures in rural areas :
Gram Panchayat (Village level)Panchayat Samiti (Block level)Zila Parishad (District level)
Jharkhand Panchayati Raj Act, 2001
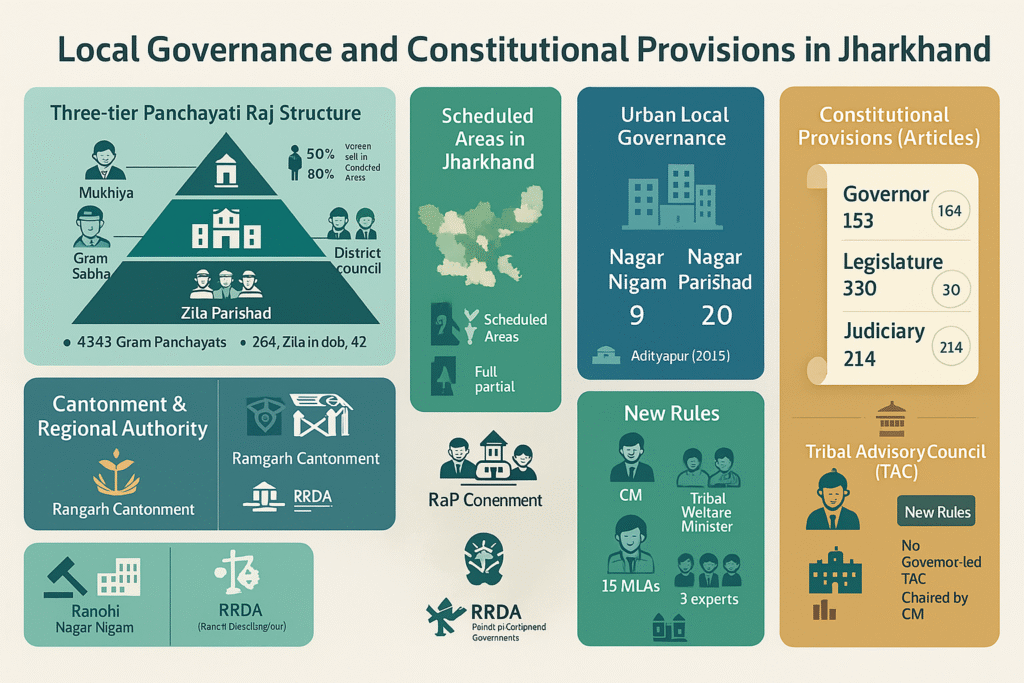
Enforced in 2001 , this Act introduced the three-tier Panchayati Raj system in Jharkhand.
Reservation Provisions :
80% reservation for Scheduled Tribes in notified areas.*50% reservation for Scheduled Tribes in non-notified areas.*50% reservation for women candidates across all categories.*
Notified Scheduled Areas in Jharkhand (as per Presidential Order, 2007)
The following 16 districts are notified as Scheduled Areas under the Fifth Schedule of the Indian Constitution:
Fully Notified (13):
Ranchi
Khunti
Lohardaga
Gumla
Simdega
Latehar
West Singhbhum
East Singhbhum
Dumka
Jamtara
Sahibganj
Pakur
Seraikela-Kharsawan
Partially Notified (3):
Total number of notified blocks: 131 *
Structure of the Three-Tier Panchayati Raj
Village Level – Gram PanchayatBlock Level – Panchayat SamitiDistrict Level – Zila Parishad
Gram Panchayat (Village Council)
Primary and lowest level institution under Panchayati Raj.One Gram Panchayat for every 5,000 rural population .Currently, Jharkhand has a total of 4,345 Gram Panchayats , all operational.
Among these, 2,074 are notified Panchayats with all seats reserved for ST candidates.
Composition & Election
One Panchayat Member per 500 population .
Elections are held with reservations for SCs, STs, and women .
Mukhiya (Head) is the chief executive of the Panchayat.Up-Mukhiya (Deputy Head) supports in absence of the Mukhiya.
Election & Tenure
Mukhiya is directly elected by the village electorate.*Mukhiya’s tenure is 5 years .
Mukhiya can be removed by a two-thirds majority through a no-confidence motion. In Mukhiya’s absence, the Up-Mukhiya takes over but:
Cannot hold office beyond 6 months . After 6 months, fresh election for Mukhiya is mandatory.
Panchayat Sevak (Secretary): Appointed by the government, acts as liaison between the state and villagers.
Functions of Gram Panchayat
Divided into six broad categories:
Administrative Functions Law and Order Maintenance Developmental Works Welfare Activities Commercial Services Civic Utility Services
Sources of Revenue for Gram Panchayat
Taxes and Levies (local imposition)Grants from State Government Voluntary Donations from individuals/institutions
Four Key Components of Gram Panchayat System
Component Role Gram Sabha Legislature – community’s general body Gram Panchayat Executive – policy and implementation Gram Kachahari Judiciary – village-level justice Gram Raksha Dal Policing and community safety
Gram Sabha (Village Assembly)
Composed of all adult voters of the village.
One Gram Sabha per village, even if a Panchayat covers 2–3 villages.
Powers & Duties :
Approves administrative proposals of the Panchayat.
Holds elections for Panchayat members.
Monitors Panchayat activities — acts as a watchdog. *
Gram Kachahari (Village Court)
Resolves minor civil and criminal cases .
Headed by Sarpanch (elected directly).
Composed of 9 members , including Sarpanch.
One Up-Sarpanch is elected internally to assist or substitute the Sarpanch.
Panchayat Mukhiya or executive members cannot be Kachahari members. Tenure of Kachahari members: 5 years
Important Facts Frequently Asked in Exams
Jharkhand Panchayati Raj Act was enacted in 2001. Reservation of 80% in notified and 50% in non-notified areas for STs. 50% reservation for women in Panchayati Raj institutions. 131 blocks and 16 districts are currently notified as Scheduled Areas. Total of 4,345 Gram Panchayats, with 2,074 notified for STs. Direct election of Mukhiya and Sarpanch. No-confidence motion requires 2/3 majority.
Gram Kachahari (Village Court)
Handles civil and criminal cases up to ₹10,000 .Empowered to impose simple imprisonment (up to 1 month) and fines *up to ₹1,000 .
In case of non-payment of fine, imprisonment can be extended by 15 days .
Gram Raksha Dal (Village Defence Force)
Serves as the village-level police body .
Comprises youths aged between 18 and 30 .
The leader is called the Dalpati , appointed on the recommendation of the Mukhiya and executive members.
Functions:
Maintain peace and law & order.
Safeguard the village and assist during emergencies and crises .
Panchayat Samiti (Block-Level Governance)
Second (intermediate) tier in the Panchayati Raj hierarchy.Set up at the block level ; named after the respective block.
All 264 blocks in Jharkhand have functional Panchayat Samitis.
131 blocks are notified and all their seats are reserved for Scheduled Tribes (STs).
Composition of Panchayat Samiti
Elected Members : 1 member per 5,000 population Ex-Officio Members :
All Mukhiyas elected from the block area.
Associate Members :
MLAs, MPs (Lok Sabha & Rajya Sabha) elected from the block.
Leadership & Tenure
The head of the Panchayat Samiti is called Pramukh , assisted by an Up-Pramukh .
Both are elected from among the members.
Term: 5 years for both.Can be removed through a 2/3rd majority no-confidence motion . Block Development Officer (BDO) serves as the ex-officio secretary of the Panchayat Samiti.
Executes decisions.
Participates in meetings but has no voting rights .
Functions of Panchayat Samiti
State-Directed Functions : Implementation of state-sponsored development programs.Community Development Programs :
Agriculture, irrigation
Animal husbandry & fisheries
Cottage industries
Education, health, welfare
Supervisory Functions :
Review of Gram Panchayat activities Modification of Gram Panchayat budgets Levy of new taxes Supervision of BDO’s work
Sources of Revenue
Grants from the state government. Land revenue and other local taxes.
Zila Parishad (District-Level Governance)
Third and apex tier of the Panchayati Raj system.Established at the district level , named after the respective district.
All 24 districts in Jharkhand have functional Zila Parishads.
13 districts are fully notified and3 are partially notified , with reservation of all seats for STs in fully notified districts.*
Composition of Zila Parishad
Elected Members : 1 per 50,000 population Ex-Officio Members : All Pramukhs from the district.Associate Members : Elected MLAs, MPs (Lok Sabha & Rajya Sabha) from the district.
Leadership & Tenure
The head is the Adhyaksh (Chairperson) , supported by an Upadhyaksh (Vice-Chairperson) .
Both are elected from within.
Tenure: 5 years .Adhyaksh can be removed via 2/3rd no-confidence vote or by State Government . Deputy Development Commissioner (DDC) is the ex-officio secretary :
Convenes meetings on Chairperson’s orders.
Acts as chief adviser and coordinates committee work.
Functions of Zila Parishad
Advisory Functions : Planning & execution of district-level development and government-assigned projects.Financial Functions :
Reviewing Panchayat Samiti budgets
Approving funds
Disbursing state and central funds to Samitis
Coordination & Supervision :
Oversight of block-level development plans
Civic Services Welfare Functions Developmental Activities
Sources of Revenue
Grants from the state for development programs.
General financial grants from the government.
Share from land revenue and local taxes.
Jharkhand Panchayati Raj (Amendment) Ordinance – 2021
Applies across the state excluding municipal areas. In case Panchayat elections are delayed due to a pandemic , the ordinance:
Allows extension of tenure for elected Panchayat representatives
Can extend tenure by 6 months or until elections are held .
Applies to both Panchayats and Zila Parishads.
Urban Local Governance in Jharkhand
Urban areas in Jharkhand are managed through Municipal Corporations, Municipal Councils, Nagar Panchayats , and Cantonment Boards .
Municipal Corporations (Nagar Nigam)
Currently, Jharkhand has 9 Municipal Corporations :
Ranchi Nagar Nigam (est. 15 Sept 1979)
Dhanbad
Deoghar
Adityapur (est. 7 Feb 2015)
Chas (est. 9 Feb 2015)
Medininagar
Hazaribagh
Mango
Giridih
Governance Structure
As per Ranchi Municipal Corporation (Incorporation & Amendment) Act, 2001 :
Provision for direct election of Mayor and Deputy Mayor . Earlier, they were elected by councillors and aldermen.
Ranchi Nagar Nigam is divided into 55 wards .
Mayor & Administration
Mayor is considered the first citizen of the city and serves as the ceremonial head .The actual administrative head is the Municipal Commissioner , appointed by the State Government .
Mayor and Deputy Mayor have 5-year terms.
Other Urban Local Bodies (ULBs)
20 Nagar Parishads (Municipal Councils) 20 Nagar Panchayats 1 Notified Area Committee (NAC) – Jamshedpur Total number of urban local bodies: 50
Gomia Nagar Parishad (Bokaro) was dissolved on 31 December 2020.
Cantonment Board
Jharkhand has only one Cantonment Board : Ramgarh
Exam-Focused Highlights
Gram Kachahari can impose up to ₹1,000 fine and one-month imprisonment. All Panchayat Raj bodies have 5-year tenures. 131 blocks are notified with 100% ST reservation. Zila Parishad exists in all 24 districts, 13 fully notified. Jharkhand has 9 Nagar Nigams and 50 total ULBs. Ramgarh is the only Cantonment Board. Panchayat elections can be postponed during emergencies (2021 ordinance).
Nagar Panchayats & Municipal Councils in Jharkhand
Nagar Panchayats – District-wise
Sl. No. Nagar Panchayat District 1 Bundu Ranchi 2 Khunti Khunti 3 Bagra Chatra 4 Domchanch Koderma 5 Barhi Sariya Giridih 6 Dhanwar Giridih 7 Hussainabad Palamu 8 Chhatarpur Palamu 9 Hariharganj Palamu 10 Nagar Untari Garhwa 11 Majhiyanv Garhwa 12 Chakulia East Singhbhum 13 Saraikela Saraikela-Kharsawan 14 Jamtara Jamtara 15 Basukinath Dumka 16 Barharwa Sahebganj 17 Rajmahal Sahebganj 18 Mahagama Godda
Nagar Parishads – District-wise
Sl. No. Nagar Parishad District 1 Gumla Gumla 2 Simdega Simdega 3 Lohardaga Lohardaga 4 Jhumri Tilaiya Koderma 5 Phusro Bokaro 6 Dhanbad Dhanbad 7 Chatra Chatra 8 Ramgarh Ramgarh 9 Bishrampur Palamu 10 Garhwa Garhwa 11 Chaibasa West Singhbhum 12 Chakradharpur West Singhbhum 13 Jugsalai East Singhbhum 14 Kapali Saraikela-Kharsawan 15 Mihijam Jamtara 16 Dumka Dumka 17 Sahebganj Sahebganj 18 Pakur Pakur 19 Godda Godda 20 Madhupur Deoghar
Other Key Facts on Urban Administration in Jharkhand
Ranchi Municipality (est. 1869) was the first municipal body in Jharkhand.Converted into Ranchi Municipal Corporation in 1979 .Ranchi Regional Development Authority (RRDA) was set up in 1975 .Master Plans for urban development and beautification.Notified Area Committee (NAC) members are nominated by the government .Chairman is always a government officer .
Jharkhand has only one Cantonment Board: Ramgarh .
Ramgarh Cantonment Board
Established under a Parliamentary Act where military stations exist.
Directly under the Ministry of Defence .The Commanding Officer is the ex-officio Chairman .
Half of the board members are elected , and half are nominated .
Constitutional Provisions Related to Jharkhand’s Governance
Governor & Executive Powers
Article Subject 153 Governor for each State 154 Executive Power of the State 155 Appointment of Governor 156 Term of Office of Governor 157 Qualifications 158 Conditions of Office 159 Oath or Affirmation 160 Discharge of functions in contingencies 161 Power to grant pardons, reprieves, etc. 162 Extent of executive power of the State 163 Council of Ministers to aid and advise the Governor 165 Advocate General for the State 166 Conduct of Government Business 167 Duties of Chief Minister 168–191 State Legislature provisions including Speaker, sessions, disqualifications
Legislative & Financial Provisions
Article Subject 196–200 Procedure for passing bills 202 Annual Financial Statement (Budget) 204 Appropriation Bills 205 Supplementary & Additional Grants 206 Vote on Account, etc. 212 No Court to inquire into proceedings of Legislature 213 Governor’s power to promulgate Ordinances
High Court & Judiciary Provisions
Article Subject 214–217 High Court structure, appointment & tenure of judges 222 Transfer of High Court Judges 223 Acting Chief Justice 225–226 Jurisdiction & power to issue writs Note : High Court judges are removable under Article 124(4) (same as Supreme Court judges).
Tribal Protection & Development – Constitutional Provisions
Article Provision 15(4) Promotion of interests of socially/economically backward classes 16(4) Reservation in employment 19(5) Reasonable restrictions on rights for tribal protection 23 Prohibition of trafficking and forced labor 29 Protection of minority interests 46 Promotion of educational & economic interests of SC/STs 164(1) Provision for Tribal Welfare Minister 330–332 Reservation for STs in Lok Sabha and State Assemblies 335 Claims of STs in public employment 338(A) National Commission for Scheduled Tribes 339 Union control over administration in Scheduled Areas
Note : Scheduled Areas and Tribal Administration provisions are covered under the Fifth Schedule of the Constitution.
Tribal Advisory Council (TAC) in Jharkhand
A new TAC rule was notified by the Jharkhand Government.
Governor’s role removed in the formation of the council.
Structure of the TAC
Ex-officio Chairperson : Chief MinisterEx-officio Vice-Chairperson : Minister of Tribal WelfareTotal Members : 20
15 ST MLAs (nominated by CM)
3 tribal subject experts (nominated by CM)
1 Government-appointed Secretary
Tenure : Co-terminus with Assembly (for MLAs); experts can be reappointed with CM’s approval.Minimum Two meetings per year , with at least 10 days’ notice .Quorum : Minimum 7 members including Chairperson.No remuneration is provided to the members.
Final Exam-Oriented Highlights
🟊 First municipality in Jharkhand: Ranchi (1869); became Nagar Nigam in 1979 .
🟊 Only one Cantonment Board: Ramgarh .
🟊 Important urban bodies: 20 Nagar Parishads, 20 Nagar Panchayats, 9 Nagar Nigams, 1 NAC (Jamshedpur) .
🟊 Tribal Advisory Council: CM is Chairperson, Tribal Minister is Vice-Chairperson .
🟊 Scheduled Areas governed under Fifth Schedule .
🟊 TAC members: 15 ST MLAs + 3 Experts + 1 Secretary .