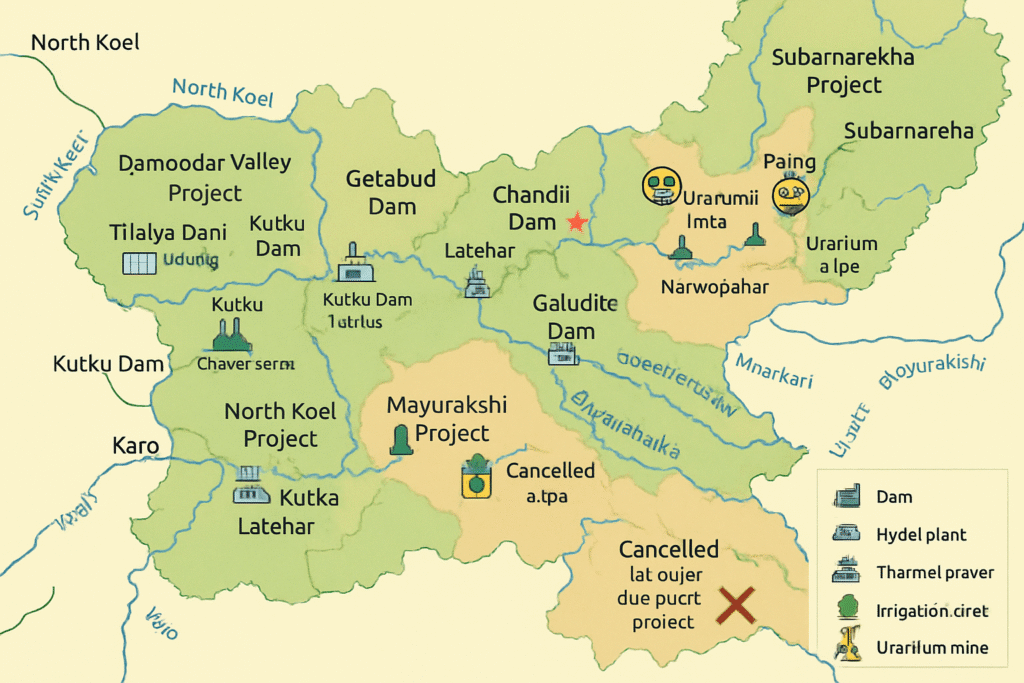
River Valley Projects in Jharkhand are multi-purpose in nature, fulfilling objectives like irrigation, flood control, power generation, and fisheries. Below is a comprehensive overview of the major river valley projects operating in Jharkhand.
What is a Multipurpose River Valley Project?
- Projects built for more than one purpose such as irrigation, hydropower, flood control, drinking water, and fisheries.
- Constructed by building dams on rivers.
- These projects are vital for the agricultural and industrial development of Jharkhand.
Damodar Valley Project (DVC) – India’s First Multipurpose River Valley Project
- Started in 1948, this was the first multipurpose river valley project in India.
- Joint venture of Jharkhand and West Bengal.
- Inspired by the Tennessee Valley Project (USA).
- Damodar Valley Corporation (DVC) was established on 7 July 1948, with its headquarters in Kolkata.
Key Infrastructure under DVC:
- 8 Major Dams
- 1 Barrage (Durgapur Barrage)
- 6 Hydel Power Plants – Tilaiya, Maithon, Bal Pahari, Panchet, Bermo, Konar
- 3 Thermal Power Stations – Bokaro, Chandrapura, Durgapur
Important Dams & Related Rivers:
| Dam Name | River | District | Catchment Area (sq. km) | Inauguration Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tilaiya | Barakar | Koderma | 984 | ⭐ 21-Feb-1953 |
| Konar | Konar | Hazaribagh | 997 | ⭐ 15-Oct-1955 |
| Maithon | Barakar | Dhanbad | 6293 | ⭐ 27-Sept-1957 |
| Panchet | Damodar | Dhanbad | 10966 | ⭐ 06-Dec-1959 |
- Other dams include:
- Bal Pahari on Barakar River
- Bermo and Panchet on Damodar River
- Bokaro Dam on Bokaro River (a Damodar tributary)
Power Capacity:
- Thermal Power: 2000 MW
- Hydel Power: 147.2 MW
- Total Power Generation Capacity: ⭐ 2147.2 MW
Irrigation:
- The project irrigates around 8 lakh hectares of land.
Subarnarekha Multipurpose Project – Supported by World Bank
- Joint project between Jharkhand, West Bengal, and Odisha.
- Started in 1982-83.
- Supported by the World Bank.
Major Dams and Sites:
| Dam Name | River | District | Year |
|---|---|---|---|
| Getalsud Dam | Subarnarekha | Ranchi | 1971 |
| Chandil Dam ⭐ | Subarnarekha | Seraikela-Kharsawan | ⭐ 1982 |
| Ichha Dam | Kharkai | Seraikela-Kharsawan, West Singhbhum | 1983 (Work halted due to protest) |
| Galudih Dam | Subarnarekha | East Singhbhum | 1983 |
| Gajia Dam | Kharkai | East Singhbhum | – |
| Palna Dam | Subarnarekha | Seraikela-Kharsawan | Proposed |
Hydel Power:
- 130 MW of electricity generated near Hundru Falls.
Environmental Concern:
- Presence of uranium mines like Narwapahar, Turamdih, and Baghjata near the river.
- Causes radioactive waste discharge, leading to serious water pollution.
Mayurakshi Project – Canada-assisted Dam 🇨🇦
- A joint project of Jharkhand and West Bengal.
- Constructed on the Mayurakshi River.
- In 1955, Masanjore Dam (also called Canada Dam) built near Masanjore, Dumka.
- Tilpara Barrage also constructed on this river.
North Koel Project – Stalled But Important
- Proposed on North Koel River, started in 1972.
- Dam and power house construction at Kutku, Latehar district.
- Aims to provide:
- Irrigation to Garhwa and Palamu districts in Jharkhand.
- Water supply to Bihar’s Gaya and Aurangabad districts.
- Electricity generation also proposed.
Koel-Karo Project – Discontinued Due to Protest
- Proposed on South Koel River and its tributary Karo River.
- Project scrapped in 2003 due to public opposition and land displacement issues.
Key Exam-Focused Facts (Frequently Asked in Jharkhand Exams):
- DVC (1948) – India’s first multipurpose river valley project.
- Chandil Dam – Frequently asked; part of Subarnarekha project.
- Masanjore Dam (1955) – Built with Canadian aid on Mayurakshi River.
- Total power generation of DVC in Jharkhand – ⭐ 2147.2 MW
- Subarnarekha Uranium Issue – Radioactive pollution concern.
- Koel-Karo Project – Cancelled in 2003 due to mass protests.
- Ichha Dam – Work stopped due to resistance.
